What Is Laminated Fabric and How Is It Manufactured
Laminated fabric has become an essential material across various industries, from fashion and sportswear to medical textiles and industrial applications. Its unique construction provides durability, waterproofing, breathability, and versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of products. Understanding what laminated fabric is, its manufacturing process, types, benefits, and applications can help designers, manufacturers, and consumers make informed choices about its use. This article explores all these aspects in detail.
Understanding Laminated Fabric
Laminated fabric is a composite material created by bonding two or more layers of fabric with additional materials such as films, foams, or membranes. The lamination process enhances the fabric’s performance by combining the properties of different layers into a single material. Typically, a textile layer provides strength, flexibility, and aesthetic appeal, while a laminated layer contributes functional characteristics such as waterproofing, thermal insulation, or chemical resistance.
The lamination process ensures that these layers act as a cohesive unit, allowing laminated fabrics to withstand stress, environmental conditions, and repeated use. Laminated fabrics can be soft and flexible for clothing applications or rigid and durable for industrial and medical uses.
The Importance of Laminated Fabrics
Laminated fabrics have gained widespread popularity because they provide a balance between comfort, functionality, and durability. In clothing, they protect against rain, wind, and cold while remaining lightweight and breathable. In industrial applications, laminated fabrics resist wear, chemicals, and moisture, extending product life. Laminated fabrics also allow for design flexibility, enabling manufacturers to create multi-functional materials for various applications.
The versatility of laminated fabrics makes them essential in sectors like sportswear, outdoor gear, medical textiles, automotive interiors, upholstery, and protective clothing. By understanding their composition and manufacturing process, designers can select the appropriate laminated fabric to meet performance and aesthetic requirements.
Types of Laminated Fabric
Waterproof Laminated Fabrics
Waterproof laminated fabrics are commonly used in rainwear, outdoor gear, tents, and medical garments. They typically combine a textile layer with a waterproof film such as polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The lamination prevents water penetration while maintaining flexibility and comfort.
Breathable Laminated Fabrics
Breathable laminated fabrics are engineered to allow moisture vapor to escape while preventing liquid water from passing through. This is achieved by using microporous membranes laminated to textile layers. These fabrics are ideal for sportswear, outdoor clothing, and protective medical garments, providing comfort and moisture management during use.
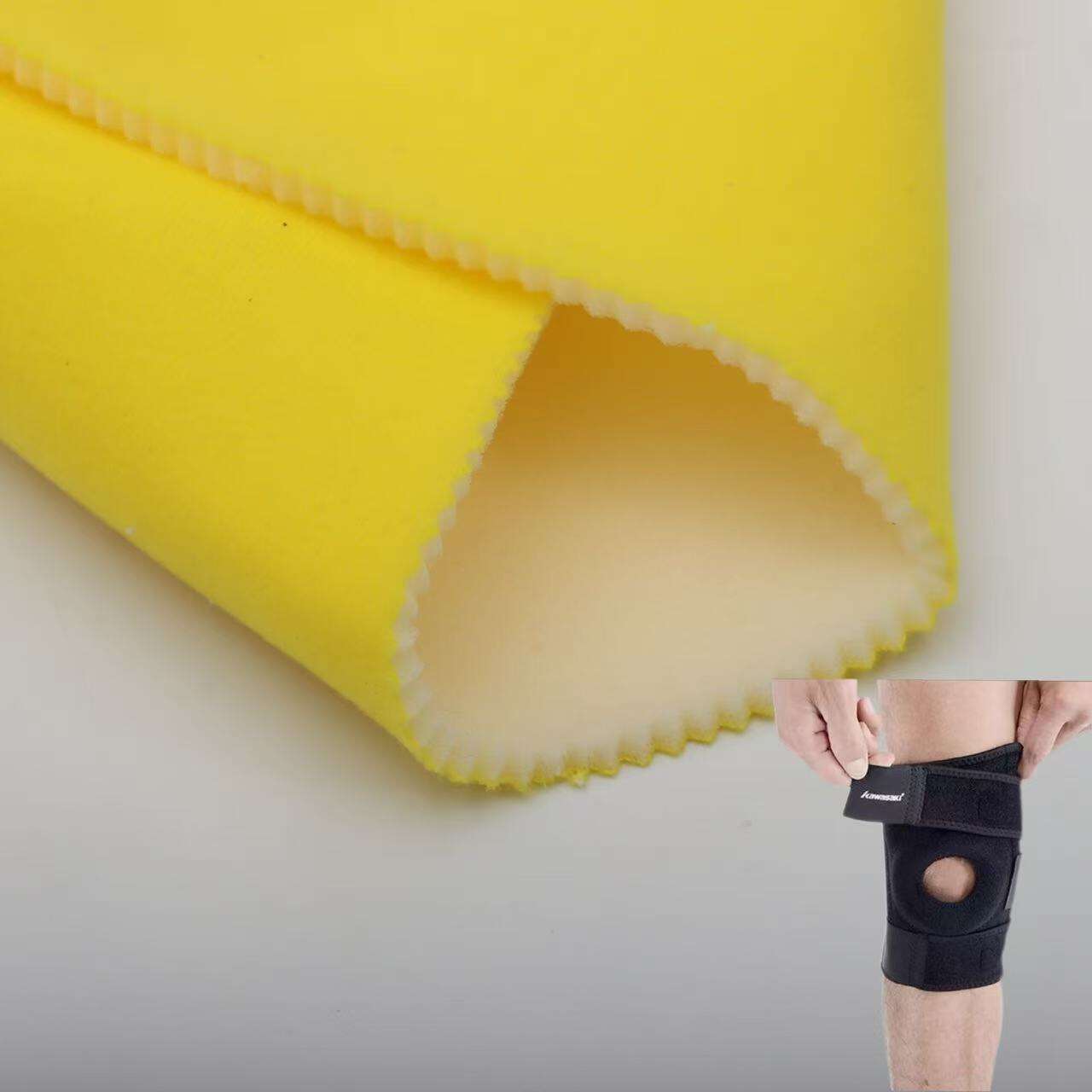
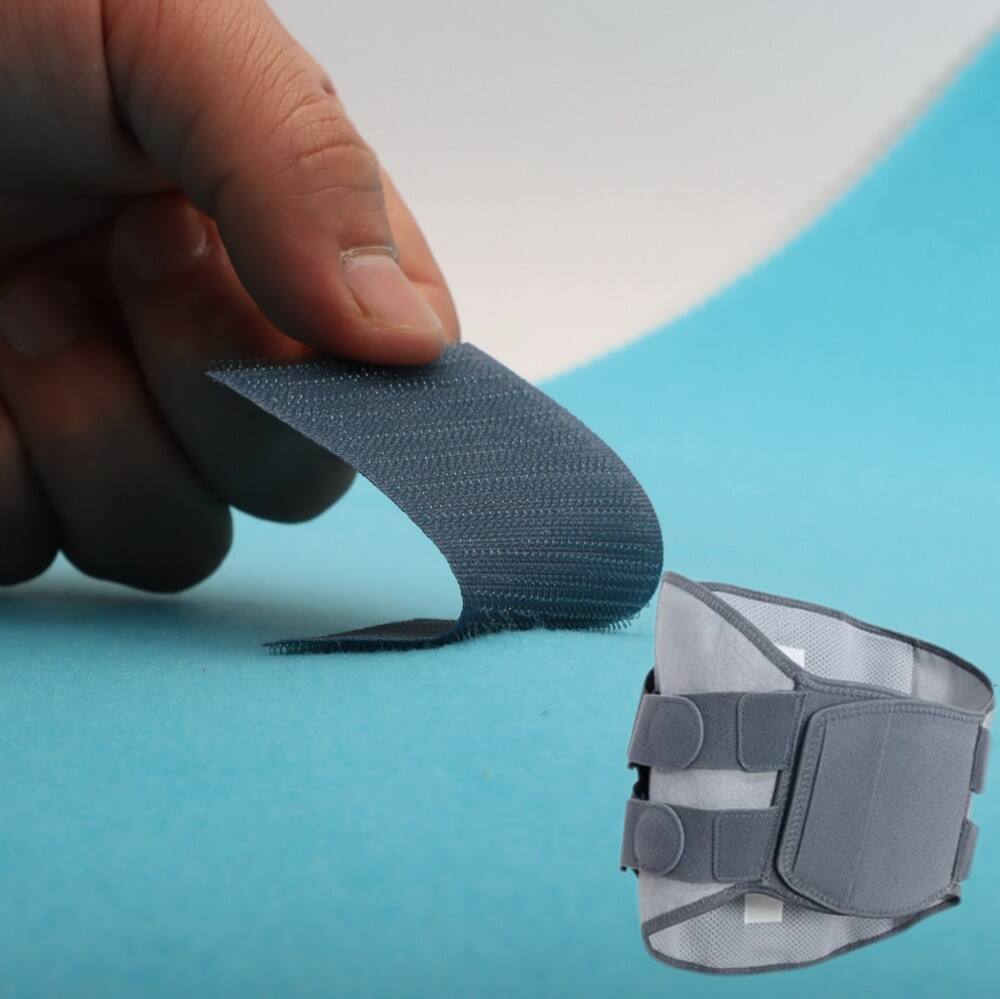
Foam Laminated Fabrics
Foam laminated fabrics incorporate a foam layer between textile layers to add cushioning, insulation, or padding. These fabrics are widely used in medical belts, orthopedic supports, protective gear, and some fashion applications where comfort and structure are required.
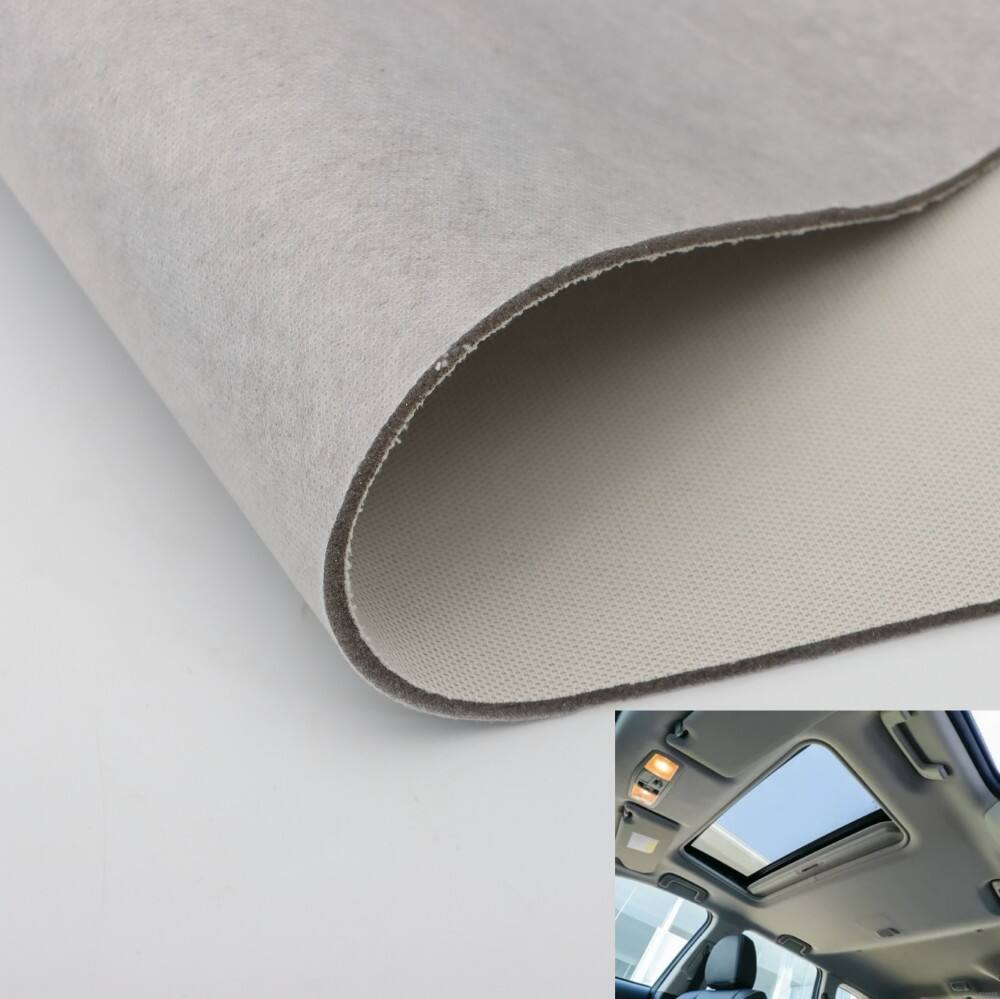
Laminated Technical Fabrics
Technical laminated fabrics are designed for industrial, automotive, and safety applications. They can combine multiple layers, including textiles, films, and protective coatings, to resist chemicals, heat, abrasion, and UV exposure. These fabrics provide durability and performance in demanding environments.
Laminated Fashion Fabrics
In fashion, laminated fabrics are used to create garments that are water-resistant, windproof, or insulated while maintaining style and drape. Designers often use thin, flexible films laminated to cotton, polyester, or nylon to achieve a balance between functionality and aesthetic appeal.
The Lamination Process
Laminating fabric involves bonding different layers using heat, pressure, adhesives, or extrusion techniques. The process depends on the type of layers, desired properties, and end-use requirements.
Heat Lamination
Heat lamination involves applying heat and pressure to bond a film or membrane to a fabric layer. The heat melts or activates the adhesive properties of the lamination material, creating a permanent bond. This method is commonly used for waterproof, breathable, and protective fabrics.
Adhesive Lamination
Adhesive lamination uses liquid or solid adhesives to bond the layers together. The adhesive is applied to one or both surfaces, followed by pressing and curing. This method is suitable for combining fabrics with foam or film layers that cannot withstand high heat.
Extrusion Lamination
Extrusion lamination involves melting a thermoplastic material and applying it directly onto the fabric surface. As the molten material cools, it forms a solid bond with the fabric, creating a durable laminated composite. This technique is often used in industrial and technical fabrics requiring high strength and chemical resistance.
Hot-Melt Lamination
Hot-melt lamination uses a thermoplastic adhesive in film or powder form, which is activated by heat and pressure. This technique allows precise control over the thickness and distribution of the adhesive, producing a strong and flexible laminated fabric.
Ultrasonic and Pressure Lamination
Ultrasonic lamination uses high-frequency vibrations to bond layers without adhesives or excessive heat. Pressure lamination can also be used to enhance the bond between layers. These techniques are increasingly used in medical and high-performance applications where precision and minimal material alteration are critical.
Advantages of Laminated Fabrics
Enhanced Performance
Laminated fabrics combine the strengths of multiple materials, providing enhanced durability, waterproofing, insulation, or chemical resistance. They are designed to meet specific performance requirements for diverse applications.
Comfort and Flexibility
Even with added functional layers, laminated fabrics can remain flexible and comfortable, especially when breathable membranes or soft foams are used. This makes them suitable for garments and wearable applications.
Design Versatility
Laminated fabrics can be customized in color, texture, thickness, and finish, allowing designers to create products that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. Multiple layers can be engineered to provide selective properties in different areas of the fabric.
Longevity
By protecting underlying fabric layers, lamination enhances the lifespan of the material. Laminated fabrics resist wear, UV exposure, moisture, and chemical damage better than unlaminated textiles.
Seamless Integration
Some lamination techniques allow the creation of seamless composites that reduce the need for stitching or sewing, enhancing water resistance, comfort, and durability.
Applications of Laminated Fabrics
Outdoor Apparel
Waterproof and breathable laminated fabrics are widely used in jackets, pants, raincoats, and outdoor gear. These fabrics keep wearers dry and comfortable during extreme weather conditions.
Medical Textiles
Laminated fabrics are integral to medical belts, wraps, protective gowns, and surgical drapes. Foam-laminated and breathable laminated fabrics provide comfort, support, and hygiene in clinical settings.
Automotive and Industrial Uses
Technical laminated fabrics are used in vehicle interiors, protective clothing, and industrial equipment covers. They resist heat, abrasion, and chemical exposure, ensuring long-term durability.
Fashion and Lifestyle Products
In fashion, laminated fabrics are used for water-resistant coats, fashion accessories, and high-performance activewear. Foam lamination adds comfort and structure to lingerie, padded clothing, and shoes.
Sports and Protective Gear
Laminated fabrics are widely employed in sportswear, protective pads, helmets, and gloves. The combination of flexibility, cushioning, and durability enhances performance and safety.
Future Trends in Laminated Fabric Manufacturing
Sustainability is a growing focus in laminated fabric production. Eco-friendly films, recycled textiles, and low-emission adhesives are becoming standard. Advances in digital lamination and precise extrusion techniques allow for thinner, lighter, and more versatile laminated fabrics. Smart textiles integrating sensors or conductive films are also emerging, enabling monitoring of temperature, pressure, or movement.
Innovation in breathable membranes, antimicrobial coatings, and flame-retardant laminates is further expanding the functionality of laminated fabrics across medical, industrial, and fashion sectors.
Conclusion
Laminated fabric is a versatile material that combines multiple layers to deliver enhanced performance, comfort, and durability. Through various lamination processes such as heat, adhesive, extrusion, and hot-melt techniques, manufacturers can produce fabrics suitable for diverse applications, including fashion, sports, medical textiles, and industrial uses. By understanding the types of laminated fabrics, their advantages, and applications, designers and manufacturers can select the right materials to meet functional and aesthetic goals. Laminated fabrics continue to evolve, offering innovative solutions for modern challenges in textile design and performance.
FAQ
What is laminated fabric?
Laminated fabric is a composite material made by bonding two or more layers of textile with films, foams, or membranes to provide enhanced durability, waterproofing, or other functional properties.
How is laminated fabric manufactured?
It can be manufactured using heat lamination, adhesive lamination, extrusion lamination, hot-melt lamination, or ultrasonic and pressure lamination depending on the materials and desired properties.
What are the main benefits of laminated fabrics?
They offer enhanced performance, comfort, flexibility, design versatility, longevity, and seamless integration.
Where is laminated fabric commonly used?
Applications include outdoor apparel, medical textiles, automotive interiors, protective gear, and fashion products.
Can laminated fabrics be breathable and comfortable?
Yes, breathable membranes and foam-laminated layers allow laminated fabrics to remain comfortable for extended wear while maintaining functional properties like waterproofing.







